English and the Four Pieces Limit
English As The Language Of AI
AS a natural language, English has both breadth and depth. You can talk about the psychology of humans, the aurora, the latest on quantum entanglement, what time the bus comes. It is a very powerful all-purpose language.
It does have drawbacks – the use of a word for many different meanings. A word can mean a noun or a verb (thousands of them), or an adverb or a preposition (the car turned on a dime, he turned on the light).
In comparison:
LLM (Large Language Model)
This approach knows nothing about what words mean. You can set up a prompt, and it will return a piece of text from the internet or other pre-processed source by matching word patterns. LLMs do not create objects to represent the words in the text, give them attributes, and then manipulate them, or reason about them. It has a very narrow area of application – it is not suitable for autonomous cars or simulation, such as having a working model of a piece of complex text. LLMs are effectively an amusing toy.
NeuroSymbolics
This is an AI language, intended to handle problems that can be separated into memory ( Artificial Neural Networks or ANNs) and reasoning (Symbolic Logic). Declaring ahead of time the form of problem you can handle is not a useful method for AI, as problems requiring intelligence to solve are rarely of one kind, or static.
Here is a small part of the Road User Handbook.
Children
Children have not developed the skills to understand and react to danger. They’re still learning where to cross safely, and they can find it hard to judge the speed and distance of vehicles.
This means they can act unpredictably around traffic. Take extra care near:
• children playing, walking or riding bikes near the edge of the road
• schools, particularly when children are arriving or leaving
• school buses or school bus zones where children may be getting on or off the bus.
Note the presence of the word “unpredictably”. Words such as this rule out any possibility of LLMs or NeuroSymbolics or ANNs being of any use – a whole new control structure has to be created to predict the unpredictable – English allows this (more exactly, a competent speaker of English does this – creating a hypothetical world and then ditching it as circumstances change).
English is broad and deep – new technology or new insights into the human mind are often first written up in English.
It also does other things:
Figurative Speech – a clump of words will acquire a more general meaning – “a walk in the park” means something that is easy to do (there are about 10,000 of them, an essential source for making text easier to understand).
Elision – “a movie set” means a lot on which a movie is filmed – “a movie set in Hawaii” means a movie which is set in Hawaii – the reader’s Unconscious Mind fills in the elided words – the machine must do the same, just not unconsciously.
Concatenation of Words “the Director General of National Intelligence”, or “Anti-Money Laundering and Counter-Terrorism Financing” – in technical English, a cluster of words is used to be very specific, after which “the Director General” etc. will suffice.
Long Range Reference
Internal Reference:designated service covered by item 54 of table 1 in section 6
External Reference: under subsection 766E(1) of the Corporations Act 2001
The external references can be active – that is, they mesh with the activity in the working model of the document being analysed. Effectively, the library becomes an active structure (within limits – we are not promising the Library of Congress).
Going back to NeuroSymbolics (NS), how would it compare? It would be a nightmare to translate English into NS, particularly for hundreds or thousands of pages, and one could guarantee it would be very wrong in many different ways.
Why Isn’t AI Available Using English?
You took 20 years to learn English, and you have a brain. Computers don’t have a brain comparable in any way to yours. LLM was an attempt to improve Search Engine searching. It does that, but has no idea what the words mean, and words in English can have many meanings – take “bar” as an example. An iron bar, a wine bar, “the Bar” referring to lawyers collectively, a high-jump bar, as in “he raised the bar for semiconductor track width” (nothing to do with high jumps), so you have multiple meanings colliding with figurative speech.
It is not a reducible problem – imagine if you needed a dozen experts – one for nouns, one for verbs, one for conjunctions, etc. The first problem – is this word acting as a preposition or adverb – the car turned on a dime, he turned on the light. It is a problem that needs one mind to make all the pieces work together, which means it takes a long time (twenty years – we started in 2000, after enough memory became available in the 1990s). Once solved, the result can be copied millions of times, and updated as the language grows and changes. People are very good with text as long as it is not too complex, but fall away rapidly as the complexity increases.
A good example was the F-35. The aircraft would come off the production line, and then be pulled apart to make changes, and those changes meant it had to be pulled apart again, to make other changes, which meant … hundreds of billions of dollars were wasted because people could not understand what complex text was telling them - the Four Pieces Limit in action. Interestingly, with computers coming out their ears, they did no better than the B-52, which was also constantly being pulled apart to make changes (they at least had the excuse that computers were in their infancy then, and they were changing to jets).
A simple example- “a country road”.
“country” can mean:
Noun: the territory of a nation
A rural area
Indigenous lands
The population of a country (“the country was up in arms”)
Back country
Adjective: from or in the countryside
“Road” can mean:
A specific road
Roads in general (“back on the road again”)
A railway
A chosen path – the road to success
A sheltered area for ships
The result:
Your Unconscious Mind does this with a high degree of reliability. The Semantic AI machine has to show the same high reliability.
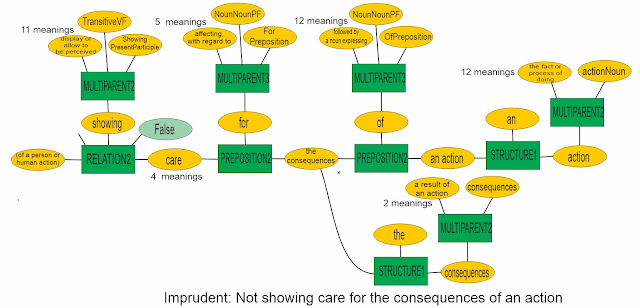
A more complex case – the many meanings of the noun “bar”.
Where there are many alternatives, as with “bar” or “set”, it will usually be easy to eliminate most possibilities (a bar of chocolate), but quite difficult to get down to a list of one – it may be necessary to read supporting materials to do so (or, embarrassingly, the machine has to ask someone).
In a complex document, which particular meaning is selected will be cause for argument - a user can see which meaning is being used, so there is no basis for ambiguity.






Comments
Post a Comment